You’ll soon be all set to begin declining nouns in Latin with the first of five noun declensions!
Use the chart and example sentences below to master the first declension.
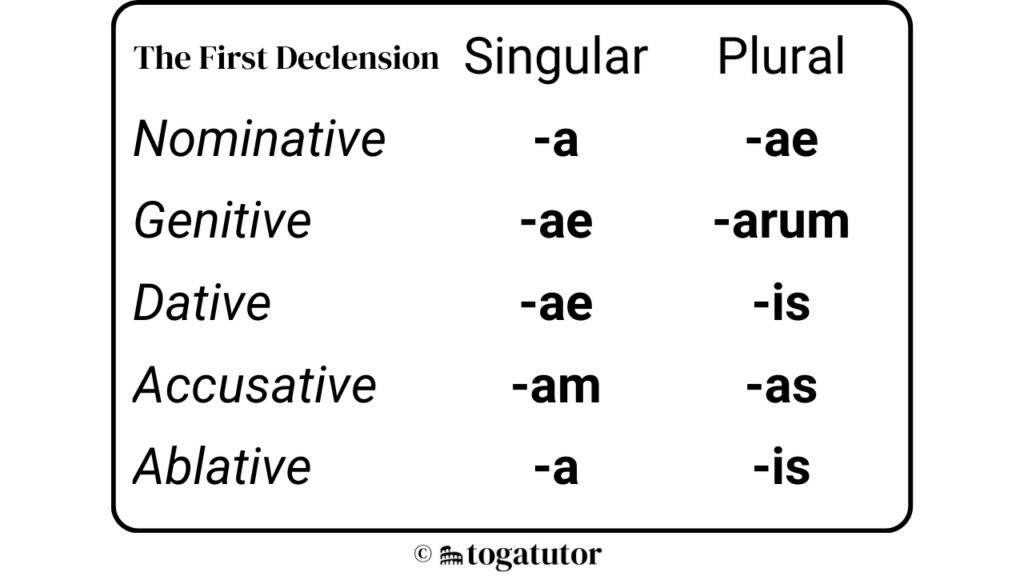
What is each case?
Nominative: The subject of a verb
Genitive: Denotes possession or close association
Dative: The indirect object, or beneficiary, of a verb
Accusative: The direct object, or the thing affected by the verb
Ablative: Usually indicates location, separation, instrument, or association
Here’s an example:
Puella sagittam agricolae nautis in villa dat. (The girl gives the arrow of the farmer to the sailors in the farmhouse.)
Puella (the girl) is in the nominative case. It is the subject of the sentence, in other words, the one doing the action.
Sagittam (the arrow) is in the accusative case. It is the direct object of the sentence, the action is being done to it, it is being given.
Agricolae (the farmer) is in the genitive case. It denotes possession of the arrow.
Nautis (the sailors) is in the dative case. The sailors are the beneficiaries of the action (giving), they receive the arrow.
Villa (the farmhouse) is in the ablative case. It goes with the preposition “in” to indicate the place that the action takes place.




